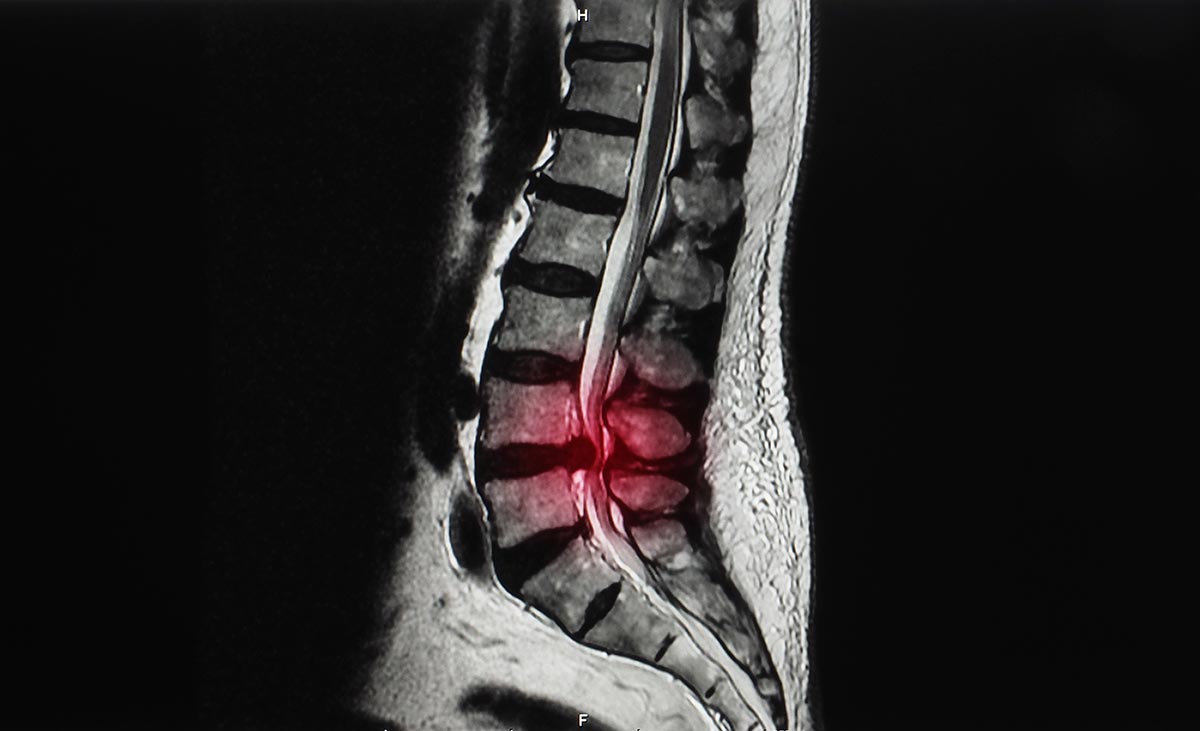
Spinal stenosis is a medical condition characterized by the narrowing of the spinal canal, which puts pressure on the spinal cord and the nerves within the spine. This narrowing can occur in different regions of the spine, such as the cervical (neck), thoracic (upper back), or lumbar (lower back) areas.
The narrowing of the spinal canal is often caused by age-related changes, such as the thickening of ligaments or the development of bone spurs, as well as conditions like herniated discs or arthritis.
The symptoms of spinal stenosis can vary depending on the location and severity of the compression, but they commonly include pain, numbness, weakness, and difficulty with balance and walking.
Treatment for spinal stenosis typically aims to relieve symptoms and improve quality of life. The specific approach may depend on the individual’s condition, the severity of symptoms, and the overall health of the patient. Here are some common treatment options:
1: Conservative management: Non-surgical treatments are usually tried first and may include:
- Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), pain relievers, and muscle relaxants.
- Physical therapy: Strengthening exercises, stretching, and low-impact aerobic conditioning.
- Epidural steroid injections: Corticosteroids are injected into the affected area to reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
2: Assistive devices: The use of assistive devices like a cane or walker can help improve balance and mobility.
3: Lifestyle modifications: Maintaining a healthy weight, regular exercise, and practicing good posture may help alleviate symptoms.
4: Surgical intervention: If conservative treatments fail to provide relief or if the condition worsens, surgery may be considered. The specific procedure depends on the location and severity of stenosis. Common surgical options include decompressive laminectomy, laminotomy, or spinal fusion.
It’s important to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for individual cases of spinal stenosis, as they can provide a more accurate diagnosis and recommend the most suitable treatment options based on the patient’s specific condition.





Leave A Comment